Project Management Life Cycle.
Introduction
In today's fast-paced business environment, managing projects effectively is crucial for organizations to achieve their goals and deliver successful outcomes. The project management life cycle provides a structured framework that guides project managers through the entire project from initiation to closure. This article will explore the key aspects of the project management life cycle, its phases, activities, and deliverables, as well as the benefits and challenges associated with its implementation.
Understanding Project Management Life Cycle
The project management life cycle is a series of phases that a project goes through from start to finish. It provides a systematic approach for managing projects and ensures that all necessary activities and deliverables are completed at each stage. By following a defined life cycle, project managers can effectively plan, execute, monitor, and control projects, leading to successful project outcomes.
Phases of Project Management Life Cycle
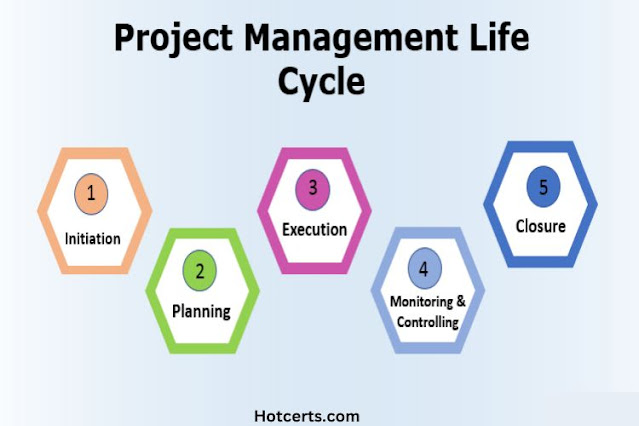
The project management life cycle typically consists of five phases: initiating, planning, executing, monitoring and controlling, and closing. Each phase has its unique set of activities and deliverables, which contribute to the overall success of the project.
1. Initiating Phase
The initiating phase marks the beginning of the project and involves defining the project's purpose, objectives, and stakeholders. Key activities in this phase include conducting a feasibility study, identifying project requirements, and obtaining stakeholder approval. The deliverables of the initiating phase include a project charter and a preliminary project scope statement.
2. Planning Phase
The planning phase focuses on developing a comprehensive project plan that outlines the project's objectives, scope, schedule, budget, and resources. Key activities in this phase include defining project milestones, creating a work breakdown structure, and identifying risks and mitigation strategies.
Project Management Life Cycle: Streamlining Your Project for Success
3. Executing Phase
The executing phase is where the project plan is put into action. It involves coordinating resources, assigning tasks to team members, and implementing the project activities according to the defined schedule. Key activities in this phase include team mobilization, task execution, and progress monitoring. The deliverables of the executing phase include completed project deliverables, regular status reports, and implemented quality control measures.
4. Monitoring and Controlling Phase
The monitoring and controlling phase ensures that the project stays on track and any deviations from the plan are identified and addressed promptly. It involves monitoring project progress, comparing it to the project plan, and taking corrective actions as necessary. Key activities in this phase include performance tracking, risk monitoring, and change control. The deliverables of the monitoring and controlling phase include updated project schedules, risk management reports, and change requests.
5. Closing Phase
The closing phase marks the completion of the project and involves finalizing all project activities, documenting lessons learned, and transitioning the project's deliverables to the stakeholders. Key activities in this phase include conducting a project review, obtaining formal acceptance of deliverables, and archiving project documentation. The deliverables of the closing phase include a final project report, lessons learned documentation and a formal project closure notice.
Benefits of Using a Project Management Life Cycle
Implementing a project management life cycle offers numerous benefits to organizations and project teams. Some of the key benefits include:
1. Improved Efficiency and Productivity: The structured approach of the project management life cycle helps in optimizing resource allocation, reducing duplication of efforts, and improving overall project efficiency and productivity.
2. Enhanced Communication and Collaboration: By following a defined life cycle, project teams have a clear understanding of project goals, roles, and responsibilities, leading to improved communication and collaboration among team members and stakeholders.
3. Effective Resource Management: The project management life cycle enables better resource planning and utilization, ensuring that resources are allocated appropriately throughout the project's phases.
Challenges in Project Management Life Cycle
While the project management life cycle provides a robust framework for project management, it is not without its challenges. Some common challenges include:
1. Scope Creep: Scope creep refers to the tendency of project requirements to expand beyond the originally defined scope. Managing scope creep requires effective change control mechanisms and proactive communication with stakeholders.
2. Resource Constraints: Limited resources, whether it's budget, personnel, or equipment, can pose challenges in meeting project objectives. Efficient resource management and prioritization are essential to overcome these constraints.
3. Stakeholder Management: Projects involve multiple stakeholders with varying interests and expectations. Effective stakeholder management is crucial to ensure their active involvement and support throughout the project.
Best Practices for Successful Project Management Life Cycle
To maximize the benefits of the project management life cycle, consider implementing the following best practices:
1. Clear Project Objectives and Scope: Define project objectives, scope, and deliverables in a clear and concise manner. This helps in setting expectations and avoiding misunderstandings later in the project.
2. Effective Communication and Stakeholder Engagement: Maintain open and transparent communication channels with project stakeholders. Engage them actively in the decision-making process and keep them informed about project progress and changes.
3. Use of Project Management Tools and Techniques: Utilize project management software and tools to streamline project planning, scheduling, and monitoring. Adopt proven techniques such as risk management, quality assurance, and change control to mitigate project risks effectively.
Conclusion
The project management life cycle provides a structured approach to managing projects from initiation to closure. By understanding the phases, activities, and deliverables associated with each stage, project managers can ensure efficient project execution, better resource utilization, and successful project

.jpg)
Comments
Post a Comment